
Dysphagia following brainstem stroke is characteristically associated with a greater likelihood of occurrence, showing signs of most severe form of dysphagia, compared to hemispheric strokes. About 15% of all patients admitted to stroke rehabilitation units experience a brainstem stroke out of which about 40%–47% of the patients suffer from dysphagia. Pharyngeal function involves numerous interacting control mechanisms that ultimately link pharyngeal contraction patterns to the adjacent oral cavity and esophagus.ĭysphagia (difficulty in eating and swallowing) is extremely common following a brainstem stroke. Swallowing mechanism is a sequential event of oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal phases that transports saliva, ingested solids, and fluid from mouth to the stomach and protects the airways during swallowing. Despite being diagnosed with a severe form of dysphagia followed by late treatment intervention, the patient had complete recovery of the swallowing function. This paper documents the severity and management approach of dysphagia in brainstem stroke, with traditional dysphagia therapy and VitalStim therapy. Dearth of literature on dysphagia and its outcome in brainstem stroke particularly lateral medullary stroke motivated the author to present an actual case study of a patient who had dysphagia following a lateral medullary infarct. In India, a study showed that 22.3% of posterior circulation stroke patients develop dysphagia.
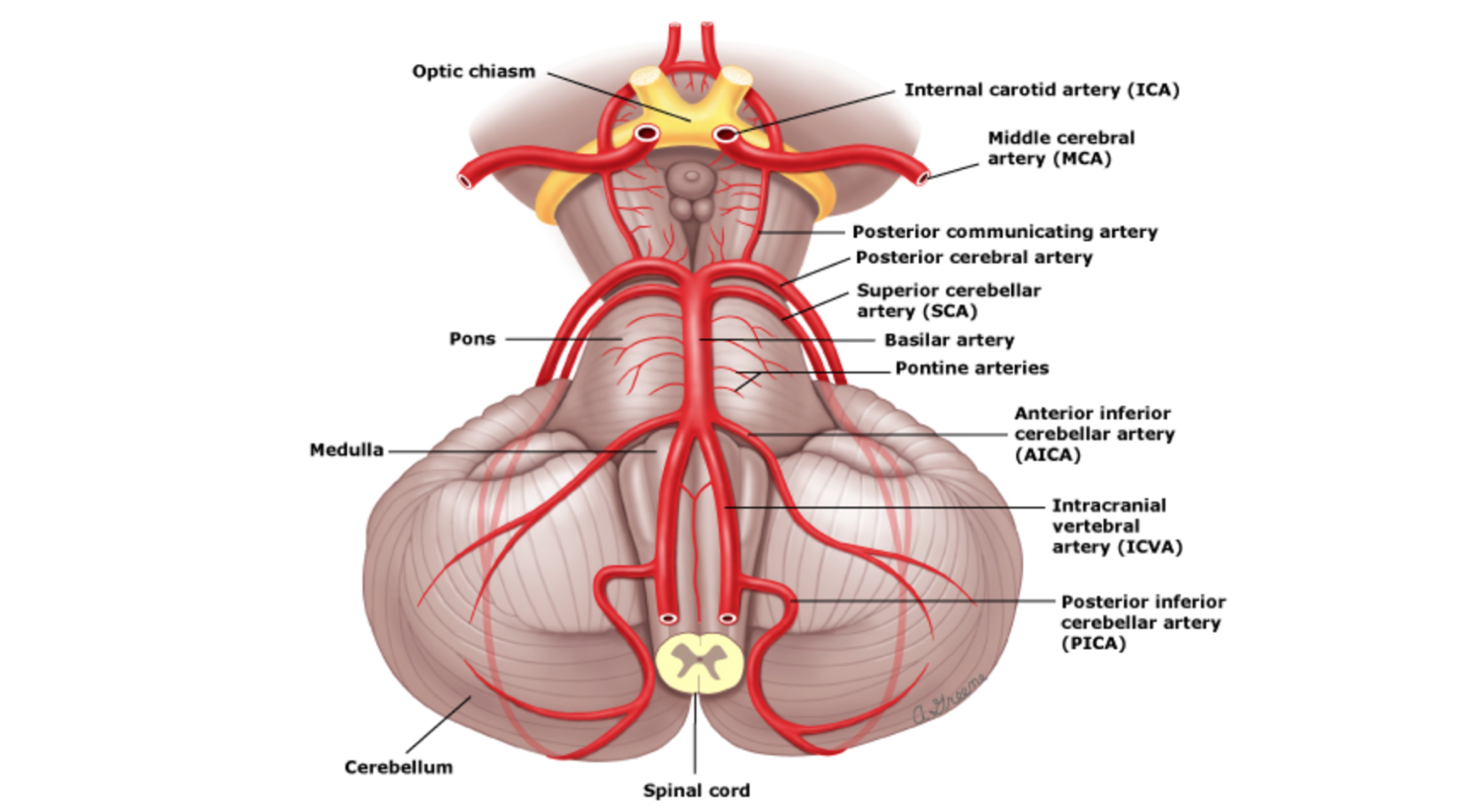
An estimated 15% of all patients admitted to stroke rehabilitation units experience a brainstem stroke out of which about 47% suffer from dysphagia.

Worldwide little research exists on dysphagia in brainstem stroke. Lateral medullary stroke is typically associated with increased likelihood of occurrence of dysphagia and exhibits the most severe and persistent form.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
